Naturally biosynthesized molecules in cannabis, known as cannabinoids, are experiencing a renaissance in pharmacological research. With over 400 studies reported on clinicaltrials.gov, cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) are among the most extensively studied for their anti-inflammatory and other pharmacological properties1. However, their low oral bioavailability presents a significant challenge, necessitating remarkably high doses that can lead to side effects such as liver damage and somnolence2.
Cannabinoid derivatives developed by Demeetra are synthetic compounds derived from natural cannabinoids. The leading candidates DM300 and DM350-P, which we call UlcerGuard Development Candidates (DCs) are purposely designed using medicinal chemistry techniques, to exhibit enhanced bioavailability and therapeutic effects, including anti-inflammatory, and anti-ulcer activities. Composition of matter intellectual property (IP) further enhances their competitive value.
Additionally, Demeetra has developed novel proprietary solid formulations. Since cannabinoids are insoluble, most oral formulations are typically oils. Oil-based formulations come with commercial challenges, including excessive costs, complex equipment requirements, and limited scalability. One common side effect of the CBD drug Epidiolex, used to treat rare forms of epilepsy, is diarrhea, which may be partly due to its oily formulation irritating the gastrointestinal tract. Our solid formulations, applicable to all cannabinoids and derivatives, offer new delayed-release options, higher drug load, improved bioavailability, reduced costs, and the potential for fewer side effects.
This page provides an overview of the efficacy and solid formulations of two cannabinoid derivatives: DM300 and DM350-P. For more information, please schedule a call and contact the Demeetra team to learn more.
Enhanced Efficacy
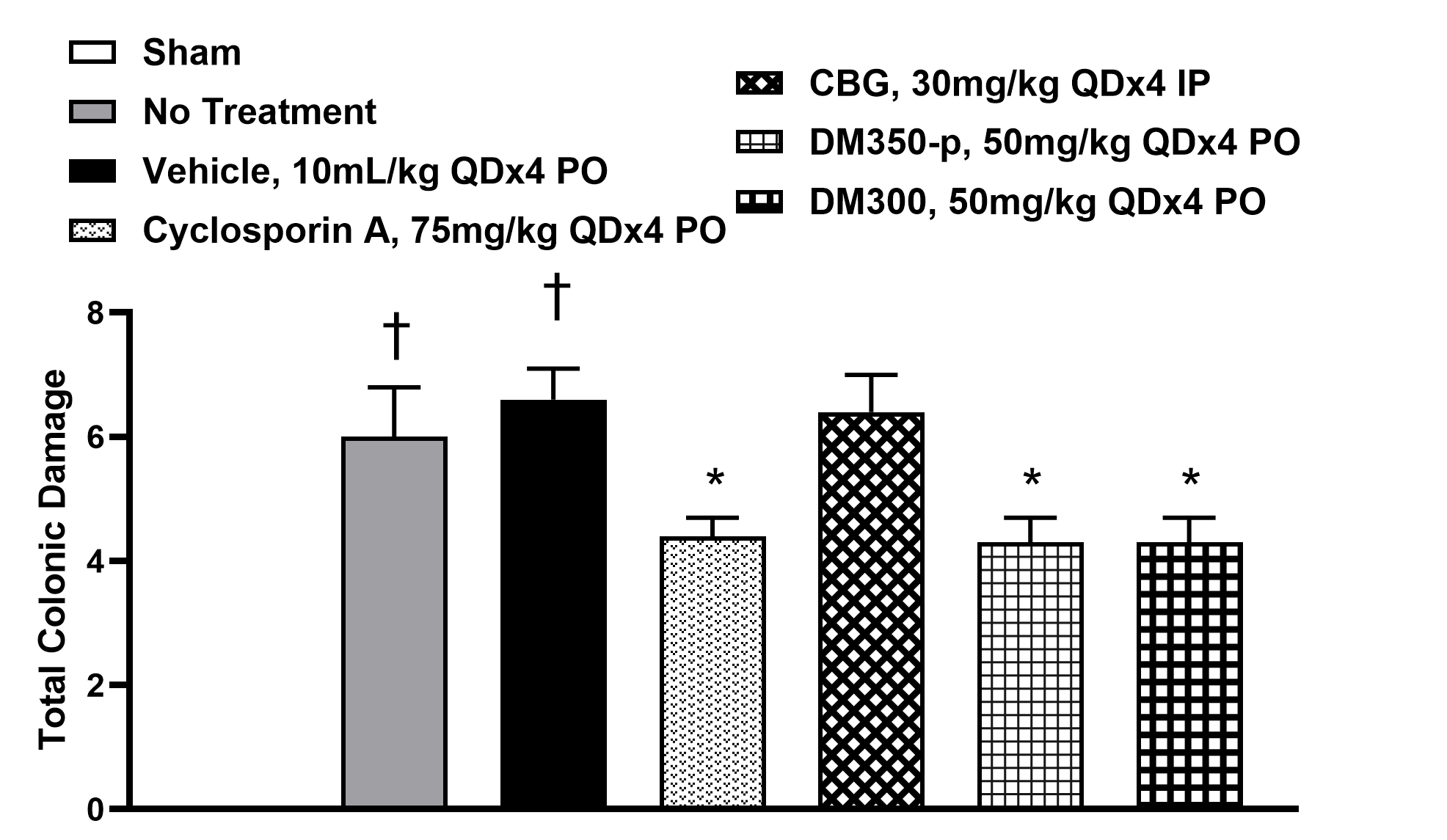
Figure 1: Total colonic macroscopic lesion score in the TNBS model: a composite of adhesions, strictures, ulcers/inflammation, and wall thickness. The positive control, DM350-P and DM300 groups all showed significant improvements over vehicle; while CBG had no effect. The positive control Cyclosporin A is not commonly used for IBD, an immunosuppressant with known side effects.
†p< 0.05, vs sham control; *p< 0.05, vs vehicle control; two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test
The mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) induced by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS), which mimics Crohn’s disease and colitis, was used to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of candidate compounds compared to CBG (labeled DM100) and a positive control Clyclosporin A. Based on the total colonic damage score (Figure 1), disease activity index, colon weight/length, and histopathology (not shown), we selected DM350-P, and DM300 for further testing.
As effective as Cyclosporin but without the immune suppression or side-effects.
Commercial Applications
- Clinical development of NCEs
- Nutraceuticals and medical foods
- Solid formulations apply to derivatives and natural cannabinoids
- New advanced delivery options
Enhanced Bioavailability
Up to 50x greater exposure compared to natural cannabinoids reduces safety risk
Broad Applications
Anti-inflammatory compounds may be applicable to many diseases and added health benefits
Indomethacin-induced Intestinal Injury Rat Model of Crohn's
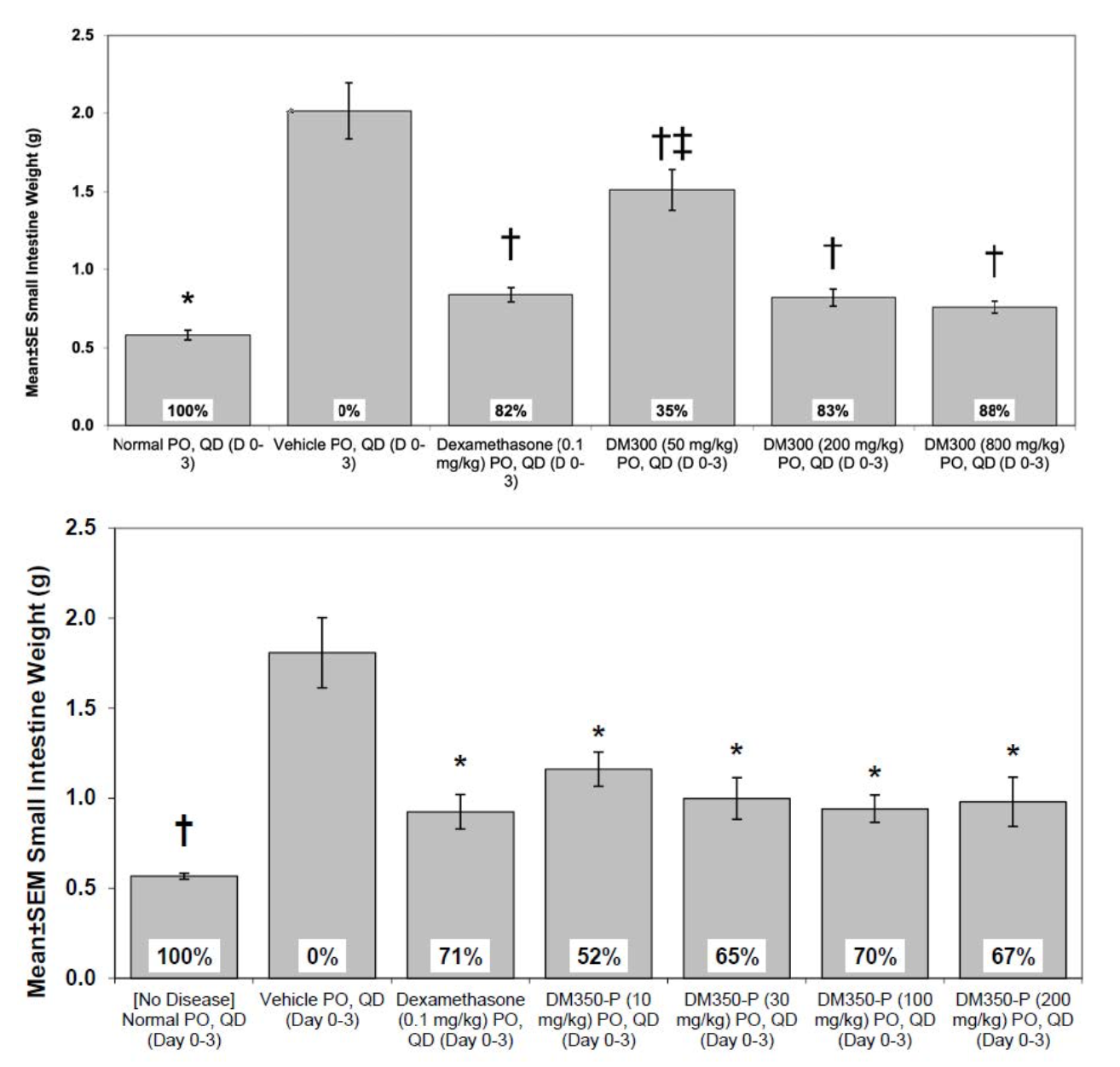
The NSAID (Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) indomethacin, induces lesions in the small bowel resembling Crohn's disease. Both DM300 and DM350-P demonstrated significant improvement in all disease parameters, including small intestine weight (Figure 2), gross score, and histopathology. Unfortunately, rats treated with CBG and DM200 experienced severe toxicity. Subsequent analysis confirmed Cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibition activity of these molecules, which may have exacerbated the NSAID-induced injury. No COX inhibition was observed in assays with DM300 or DM350-P (data not shown).
Figure 2: Small intestine weight is a simple and reliable measure of anti-inflammatory activity in the rat indomethacin-induced Crohn’s model. Both DM300 and DM350-P treatment result in significant improvement over vehicle. Notably at as low as 10 mg/kg DM350-P is close to as potent as Dexamethasone, a steroid with known side-effects. †p ≤ 0.05 ANOVA (Dunnett's post-hoc) vs. Vehicle
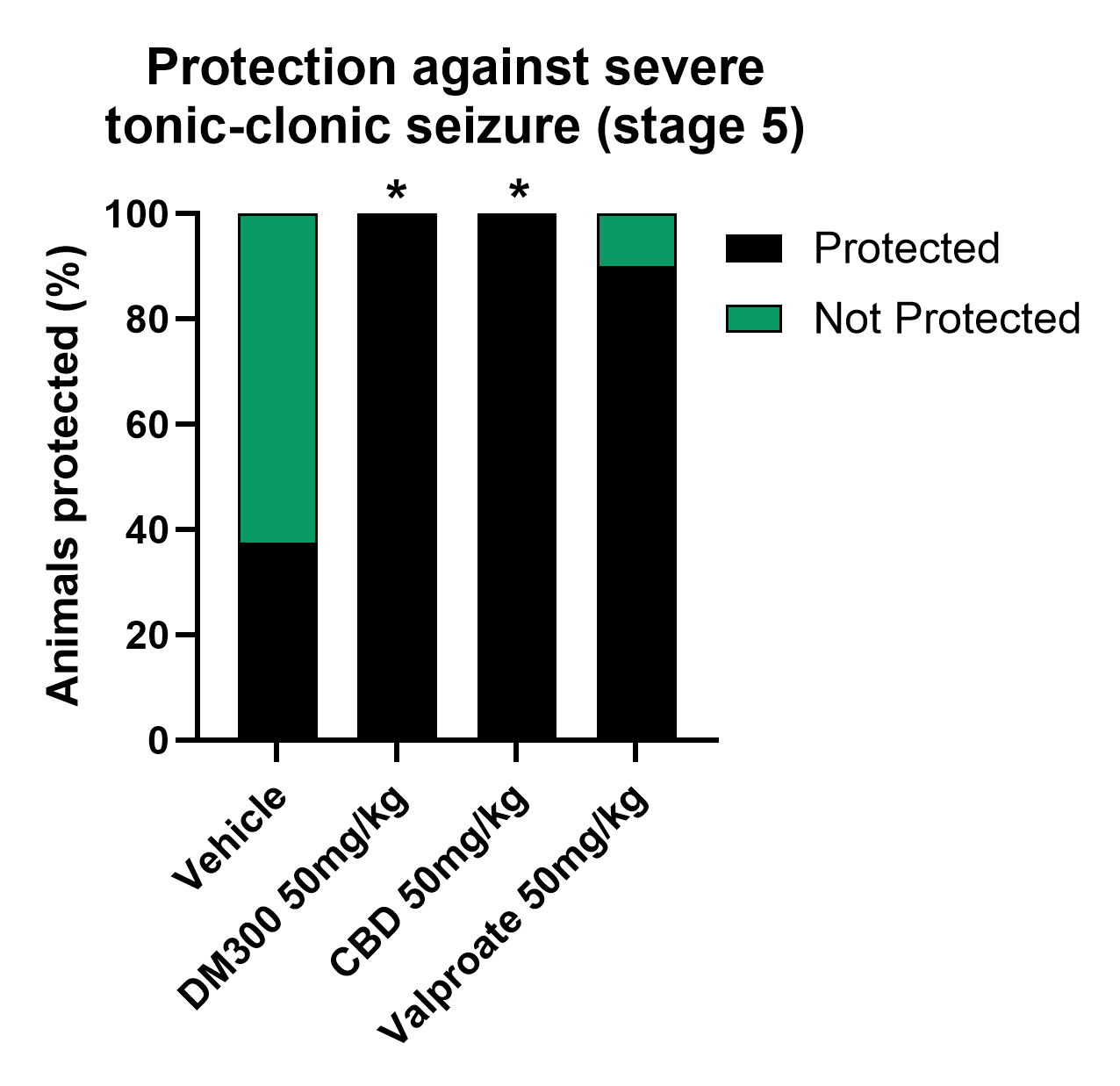
Subcutaneous pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) Seizure Model in Rat
Given CBD’s robust efficacy in rodent epilepsy models and human clinical trials, we screened DM300 and DM350-P for anti-convulsant activity in the rat PTZ seizure model. DM350-P showed lower brain exposure, resulting in significant but modest improvements (data not shown). At the lowest doses, DM300 completely eliminated severe tonic-clonic seizures in a rat model of PTZ-induced seizures. Comparable results were observed in CBD- treated rats. (Figure 3). Valproate, a popular anti-convulsive with known side effects was also tested for comparison.
DM300 demonstrates improved brain exposure compared to CBD and does not lead to any markers of liver injury. In contrast, at similar exposure levels, CBD was found to increase total bilirubin in rodents. The inhibition of the bile salt export pump (BSEP) has emerged as a significant mechanism that may contribute to increased bilirubin and the initiation of human drug-induced liver injury. In vitro studies suggested CBD inhibits BSEP while DM300 has no effect (not shown). The efficacy and lack of toxicity suggest that DM300 could be an adjuvant treatment in combination with CBD or Valproate to enhance efficacy at lower doses.
Solid Formulations
Utilizing advanced formulation techniques, Demeetra has developed a method to produce solid tablet prototypes for cannabinoids. These solid formulations demonstrate increased drug load and bioavailability compared to a sesame seed oil formulation similar to Epidiolex. Additionally, solid cannabinoid tablets bolster our IP portfolio, are expected to reduce manufacturing costs, and enable more advanced delivery options, such as delayed release.


Figures 4 + 5: Representative images of two different solid formulations in prototype tablet form. Solid formulations can reach 50% drug load.
Conclusion
DM300 and DM350-P are promising cannabinoid derivative drug candidates poised to enter IND-enabling studies. Efficacy has been demonstrated in multiple species and types of animal models of IBD and Epilepsy. They have favorable safety and PK profiles, and composition of matter IP protection. Our results indicate that medicinal chemistry can be applied successfully to cannabinoids with vast pharmacological consequences including improved therapeutic potential. These derivatives in combination with solid formulation IP demonstrate a robust drug and nutraceutical discovery and development platform.