Stable Gene Expression With piggyBac
The proven piggyBac transposase system can deliver high-yield protein production, flexibly edit any genome, rapidly screen novel strains, amplify synthetic biotechnology, and more.


Clean
Non-viral
and stable.
Flexible
Performs small to large gene integrations (200KB+)

Efficient
Cost-effective; features high expression of introduced genes.
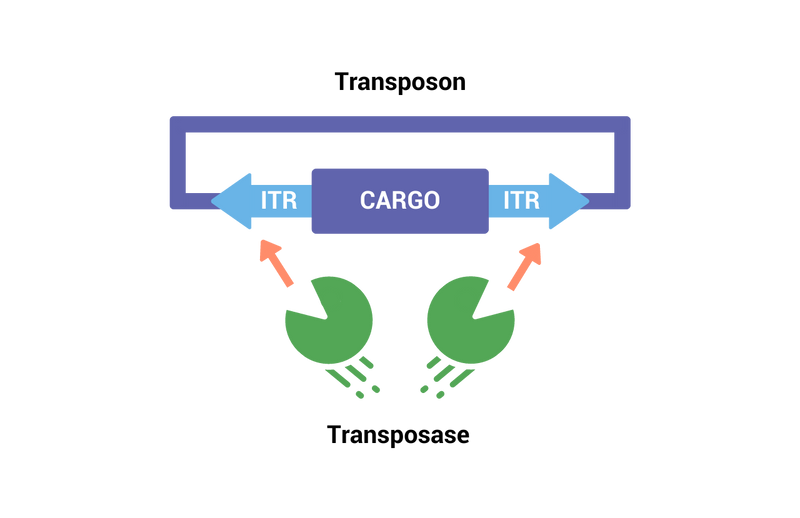
"Cut & Paste" With piggyBac Transposase + Transposon
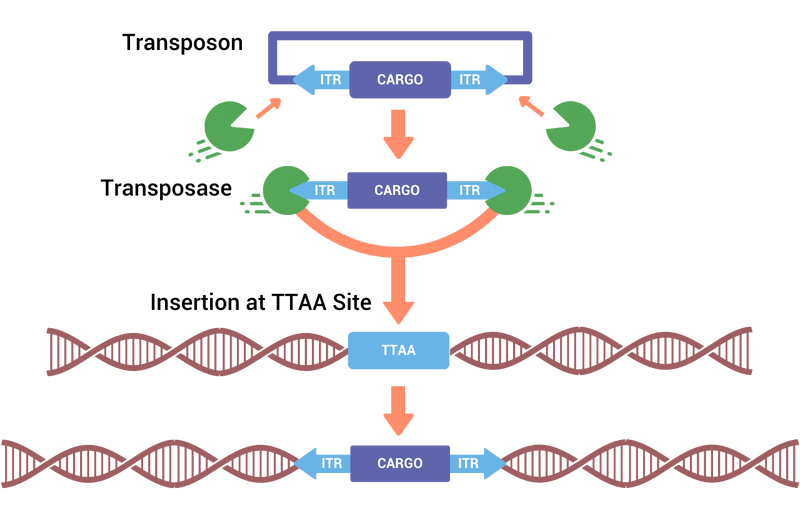
The piggyBac transposase recognizes transposon-specific inverted terminal repeat sequences (ITRs) located on both ends of the transposon vector and cuts them from the original vector. PiggyBac then integrates the expression cargo flanked by the ITRs into non-coding open chromosomal sites. This allows for the stable integration of the genes of interest at highly expressed sites in the genome.

Flexible Range Of Cargo
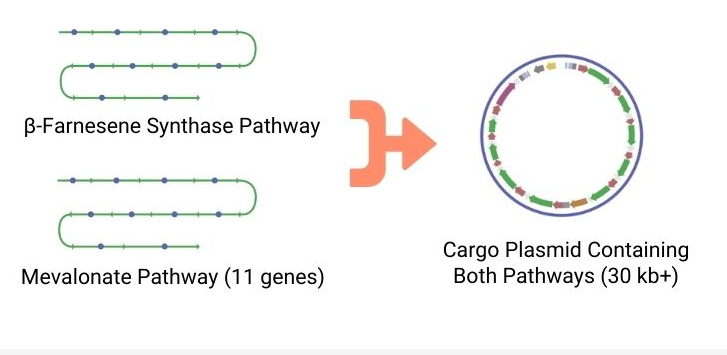
The piggyBac transposase can integrate a wide range of DNA fragment sizes, from small gene fragments up to entire metabolic pathways containing several genes (200 kb+).
A Proven Technology
The piggyBac platform has been published over 750 times with many different applications. In addition to generating cell lines with highly expressed and stable gene integration, piggyBac has been utilized to rapidly develop mutant libraries for loss and gain of function across multiple species. The integrated ITRs enable rapid mapping of the introduced genes.

Validated In Mammalian Cells, Yeast, and Plants
We specialize in multiple industries, allowing us to apply Cas-CLOVER and piggyBac technologies into broad, real world applications.

Pharmaceutical Bioprocessing
Bioprocessing and cell line engineering to produce human or non-human therapeutics
Synthetic Biotechnology
Bioprocessing and strain improvement to produce therapeutics, industrial enzymes, compounds or biofuels
Agriculture Biotechnology
Enable plant modifications that may not require GMO labels and for the production of novel therapeutics
Optimizing Your Gene Editing Research?
Contact us to learn more about our innovative gene editing technology.
